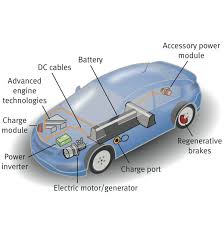
All-electric vehicles, also referred to as battery electric vehicles (BEVs), have an electric motor instead of an internal combustion engine. The vehicle uses a large traction battery pack to power the electric motor and must be plugged in to a wall outlet or charging equipment, also called electric vehicle supply equipment (EVSE). Because it runs on electricity, the vehicle emits no exhaust from a tailpipe and does not contain the typical liquid fuel components, such as a fuel pump, fuel line, or fuel tank.
Types of electric vehicles:
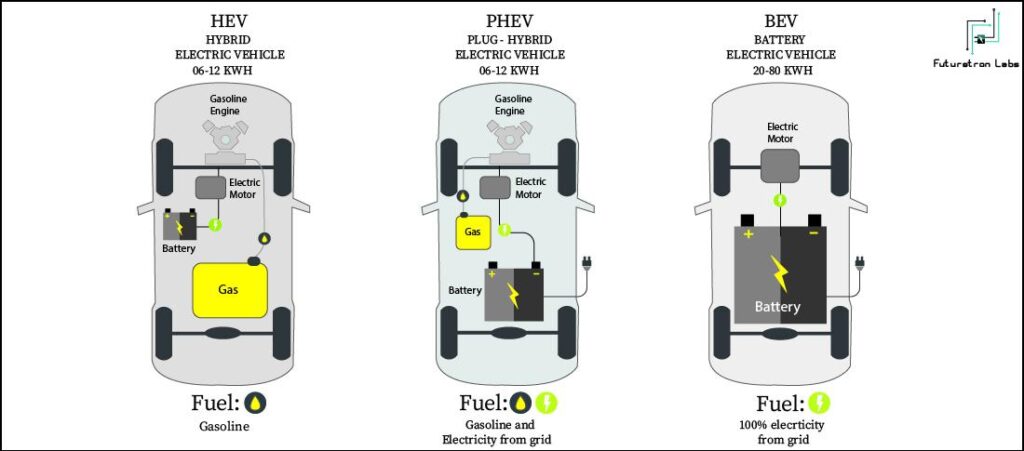
- Battery Electric Vehicle (BEV):Fully powered by electricity. These are more efficient compared to hybrid and plug-in hybrids.
- Hybrid Electric Vehicle:
- Hybrid Electric Vehicle (HEV): The vehicle uses both the internal combustion (usually petrol) engine and the battery-powered motor powertrain. The petrol engine is used both to drive and charge when the battery is empty. These vehicles are not as efficient as fully electric or plug-in hybrid vehicles.
- Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicle (PHEV): Uses both an internal combustion engine and a battery charged from an external socket (they have a plug). This means the vehicle’s battery can be charged with electricity rather than the engine. PHEVs are more efficient than HEVs but less efficient than BEVs.
- Fuel Cell Electric Vehicle (FCEV):Electric energy is produced from chemical energy. For example, a hydrogen FCEV.
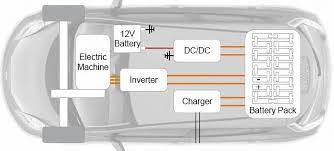
System Architecture of 4 types of electric cars is as follows:
Battery Electric Vehicles (BEVs)
BEVs are also known as All-Electric Vehicles (AEV). Electric Vehicles using BEV technology run entirely on a battery-powered electric drivetrain. The electricity used to drive the vehicle is stored in a large battery pack which can be charged by plugging into the electricity grid. The charged battery pack then provides power to one or more electric motors to run the electric car.
Hybrid Electric Vehicle (HEV):
HEVs are also known as series hybrid or parallel hybrid. HEVs have both engine and electric motor. The engine gets energy from fuel, and the motor gets electricity from batteries. The transmission is rotated simultaneously by both engine and electric motor. This then drives the wheels.
Fuel Cell Electric Vehicle(FCEV):
FCEVs are also known as Zero-Emission Vehicles. They employ ‘fuel cell technology’ to generate the electricity required to run the vehicle. The chemical energy of the fuel is converted directly into electric energy.
Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicle (PHEV):
The PHEVs are also known as series hybrids. They have both engine and a motor. You can choose among the fuels, conventional fuel (such as petrol) or alternative fuel (such as bio-diesel). It can also be powered by a rechargeable battery pack. The battery can be charged externally.

Benefits
Less pollution: By choosing to drive an EV you are helping to reduce harmful air pollution from exhaust emissions. An EV has zero exhaust emissions, but still creates a degree of greenhouse gas emissions when it is charged from the electricity grid.
Best Electric Cars in India
There are currently 30 electric cars available for sale in India. The popular electric cars are Comet EV, Tiago EV, EV6, Tigor EV, ZS EV.
Prices of Electric Cars in India
MG Comet EV. Rs7.98 – 9.98 Lakh · Tata Tiago EV. Rs8.69 – 12.04 Lakh · Kia EV6. Rs60.95 – 65.95 Lakh ·
Electric vehicles have other advantages over those powered by combustion engines:
- No fuel required so you save money on gas.
- Environmental friendly as they do not emit pollutants.
- Lower maintenance due to an efficient electric motor.
- Better Performance.
PROS & CONS of Electric Vehicles
PROS
Zero Emissions
Unlike petrol, diesel or even CNG cars, EVs produce zero tailpipe emissions. They also run quieter than conventional vehicles, which means reduced noise pollution. So, if you drive an EV, you are among the relatively few people in the world doing their bit towards making the environment cleaner and greener.
Low Maintenance
EVs are expensive to buy but cheaper to maintain. They have fewer moving parts, which reduces the chances of a breakdown . Besides, you’ll also save money on items on period maintenance such as engine oil, air filter, cooling system flushes, etc. All you have to service are the usual wear and tear components like brakes and tyres, resulting in a low maintenance cost.
Low Cost Per Kilometer
With the soaring fuel prices a petrol can be as much as 80% more costly per kilometer than recharging an electric. This difference in the daily running cost can easily make up for the higher purchase cost in the duration for the first few years depending upon your daily usage.
Good Performance
While a traditional petrol or diesel car will have an ideal engine range in which they deliver the best performance, electric cars offer exciting performance right from the start. This is particularly helpful in the city as the pickups and overtakes become effortless.
Government Subsidies
With the government encouraging the shift to EVs, there is central (FAME) and statewide subsidies on electric vehicles. This helps the prices of these EVs to be a little more competitive against internal combustion engine counterparts. In certain states, you can even get an electric vehicle at the ex-showroom price.
CONS
Limited Fast Charging Network
While there are new EV fast chargers being set up in the country, most of these are still in the pipeline. And the ones that are set up are yet to be operational. This poses a grave challenge while planning a road trip as there is no certainty whether you will find a functioning charger. Even if you do find one, having it readily available without having to wait behind others will depend on your luck.
Higher Cost
The upfront cost of buying an EV is more than petrol/diesel-powered cars. That’s because battery components are expensive and are mostly imported. However, if your daily drive is more than 50km, you should be able to recover this cost in a matter of years depending on the EV you own.
Range Limitations
Most electric cars offer a practical range between 200-300Km. This is because while they can recover range in the city with regeneration, on the highways it is only depleting. This will not be an issue if fast chargers were widely available, but that is not yet the case. And the limited numbers of these chargers make planning a road trip in an EV a cumbersome process. Also, while a lot of chargers are now listed on Google Maps, many of them are out of order.
Battery Life
While an engine of a car can go on for decades and the fuel tanks hardly ever need replacement, the life of a battery pack is limited. Just like a smartphone, the range of a battery pack keeps on depleting with use and hence, by 10 years, it depletes to about 60 percent of the total capacity. Most manufacturers give you an 8 year warranty on the battery pack but it will then need a replacement, which will be expensive. Though by then as is the case with your cell phone, you may be ready to upgrade anyways?
Limited Mass Market Options
With all the issues and challenges plaguing EVs currently, it would be prudent to buy one only if it’s your secondary car. However, there aren’t too many options to choose from, especially in the budget segment, just yet.
For more about careers in Automobile, visit on http://www.icareerkick-mgs.in
Future automobile
nourishments xyandanxvurulmus.XFQhfzdWp95Q
Your point of view caught my eye and was very interesting. Thanks. I have a question for you.
Thank you for your sharing. I am worried that I lack creative ideas. It is your article that makes me full of hope. Thank you. But, I have a question, can you help me?
thx